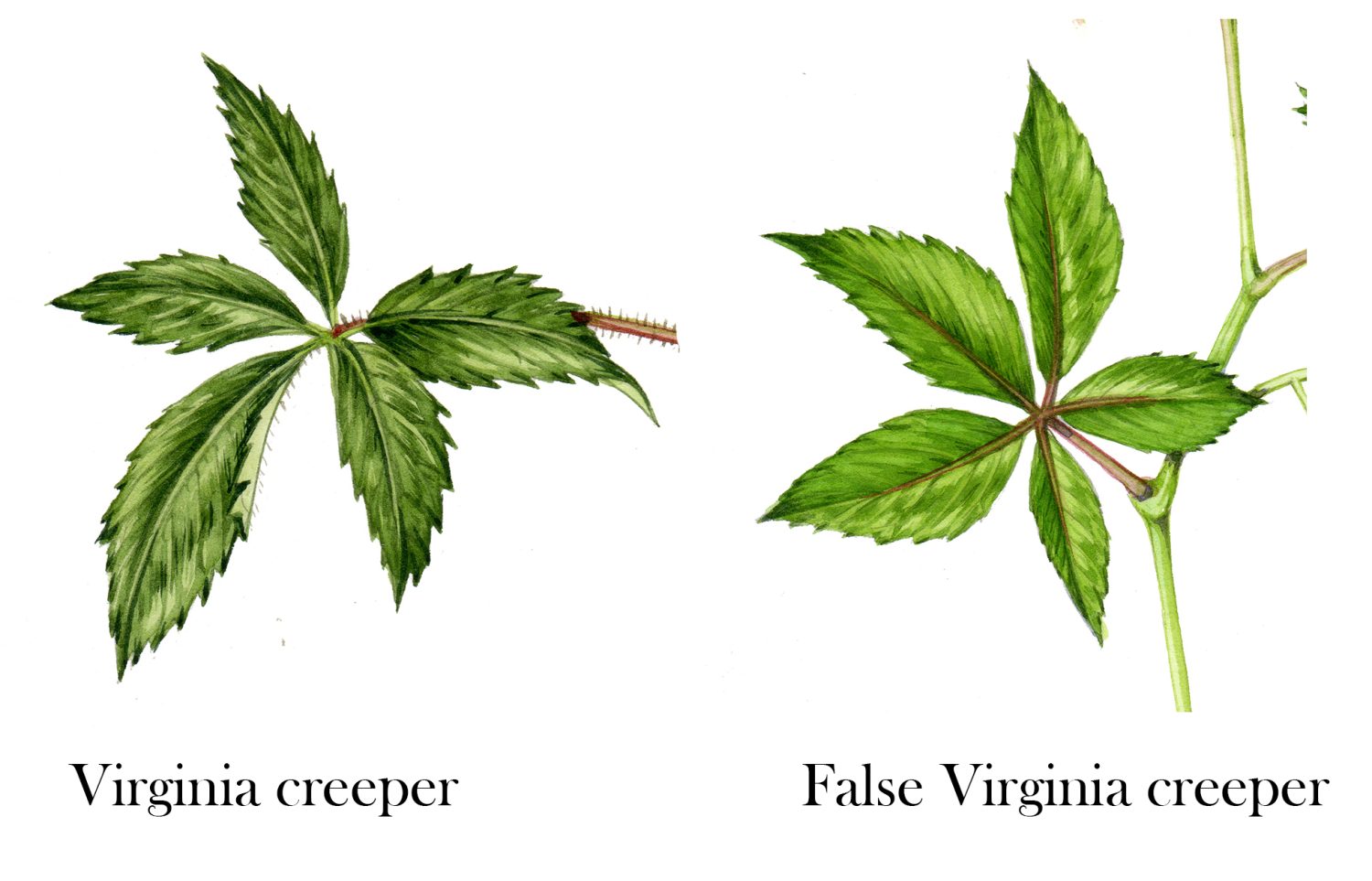
Virginia creeper (Parthenocissus quinquefolia) and false Virginia creeper (Parthenocissus inserta) are two common vines that are frequently confused. Though they share some similar characteristics, there are several key differences between these two plants that can help you distinguish between them. In this article, we’ll go over the major differences between false Virginia creeper and Virginia creeper to help you identify them.
An Overview of False Virginia Creeper and Virginia Creeper
Both false Virginia creeper and Virginia creeper are deciduous woody vines native to North America. They are favorites among gardeners for their ability to quickly cover walls, trellises, and fences with greenery.
In the fall, the leaves of both vines turn brilliant shades of red and purple, providing striking autumn foliage. This is where their similarities end, however When examined closely, several differences emerge in their growth habit, leaf shape, flowers, and stems.
Leaves: The Most Noticeable Difference
The most obvious way to tell false Virginia creeper and Virginia creeper apart is by examining their leaves and leaflets.
Virginia Creeper Leaves
- Leaves are compound with 5 leaflets (palmately compound)
- Leaflets are oval or egg-shaped with coarse, blunt teeth along the edges
- Leaves are dull green in color with fine hairs along the veins on the underside (pubescent)
- Leaf stalks are hairy
False Virginia Creeper Leaves
- Leaves are compound with 3 leaflets
- Leaflets are more triangular in shape with sharp, finer teeth along the edges
- Leaves are shiny green and hairless on the underside (glabrous)
- Leaf stalks are smooth and hairless
Flowers and Fruits
The flowers and fruits can also be used to distinguish these two vines though they are less obvious than the leaf differences.
Virginia Creeper Flowers and Fruits
- Flowers are greenish-white and borne in loose panicles, emerging from a central stalk
- Petals are not strongly reflexed backwards
- Fruits are bluish berries borne in bunches on red stalks
False Virginia Creeper Flowers and Fruits
- Flowers are greenish-yellow and borne in compact cymes without a clear central stalk
- Petals are strongly reflexed backwards
- Fruits are bluish berries in branched, dichotomous clusters on greenish stalks
Stems and Tendrils
Examining the stems and climbing tendrils can also help distinguish between false Virginia creeper and Virginia creeper.
Virginia Creeper Stems and Tendrils
- Stems are light brown and do not peel
- Tendrils highly divided into 5-8 branches and tipped with adhesive discs
False Virginia Creeper Stems and Tendrils
- Stems are reddish-brown and peel in thin strips
- Tendrils less divided (3-5 branches) and lack adhesive discs at the tips
Growth Habit and Requirements
There are also some subtle differences in the growth habits and requirements of these two vine species.
- Virginia creeper grows more rapidly and vigorously
- Tolerates a wide range of soil, moisture, and light conditions
- Can self-cling to surfaces using its adhesive tendril discs or grow supported by a trellis
- Winter hardy to USDA zone 3
- False Virginia creeper grows more slowly
- Prefers moist, humus-rich soils
- Requires a trellis or support for climbing
- Winter hardy to USDA zone 5
So in general, Virginia creeper is the more aggressive grower while false Virginia creeper grows a bit more slowly and has slightly more particular soil and moisture preferences. But their cultural requirements overlap significantly.
A Quick ID Guide
Here is a quick overview of some of the main identification points for telling apart false Virginia creeper and Virginia creeper:
Virginia Creeper
- 5 leaflets per leaf
- Coarse leaf teeth
- Dull green leaves with hairs below
- Hairy leafstalks
- Light brown non-peeling stems
- Highly divided tendrils with adhesive discs
False Virginia Creeper
- 3 leaflets per leaf
- Finer sharper leaf teeth
- Glossy green glabrous leaves
- Smooth leafstalks
- Reddish peeling stems
- Less divided tendrils without adhesive discs
How to Control These Vines in Your Landscape
While both vines provide excellent seasonal interest and color, their vigorous growth habit can sometimes lead them to spread aggressively outside of their intended space in the landscape. Here are some tips for controlling their growth and spread:
- Prune back overgrown vines in late winter to keep growth contained
- Remove suckers and new seedlings regularly
- Cut back vines growing into unwanted areas
- Consider planting in containers instead of directly in the ground
- Use plastic or metal vine barrier strips to prevent spread on fences or buildings
- Apply mulch or landscape fabric around the base to prevent new shoots from emerging
- Consider less aggressive alternatives like trumpet vine, clematis, or honeysuckle
Enjoying These Versatile Vines
Once you understand how to tell them apart, you can feel confident incorporating one or both of these vines in your landscape. Their fast growth, seasonal foliage, and ability to cover large areas makes them excellent choices for gardens, patios, fences, arbors, and other structures. Just be sure to properly identify your vine and be prepared to do some pruning and management to keep its growth in check. With a little care, false Virginia creeper and Virginia creeper can be beautiful and versatile additions to gardens across many hardiness zones.
Do you know what this plant is? Take a good look! False Virginia Creeper, Parthenocissus inserta
FAQ
Is false Virginia creeper poisonous to touch?
Should you let Virginia creeper grow on a house?
Is Virginia creeper aggressive?
Should you pull Virginia creeper?
- The Ultimate Guide to Growing Strawberries in Raised Beds - August 8, 2025
- No-Dig Garden Beds: The Easiest Way to Grow a Beautiful Garden - August 6, 2025
- How to Protect and Preserve Wood for Raised Garden Beds - August 6, 2025