If you want to start gardening and fill your space with bright flowers or fresh vegetables, starting seeds indoors is the first thing you need to do.
From choosing the right seed packet to taking care of sprouting seedlings, this post shows you the steps. It gives you the information and confidence you need to start gardening.
I will teach you the basics of seed germination, the best time to plant indoors, and how to take good care of your seedlings as they grow into strong plants that can thrive outside.
The moment a tiny green sprout emerges from the soil is magical for any gardener. However, the timing of this process can be a mystery, especially for beginners. This comprehensive guide sheds light on seed germination, explaining the factors that determine how long it takes seeds to sprout.
What is Seed Germination?
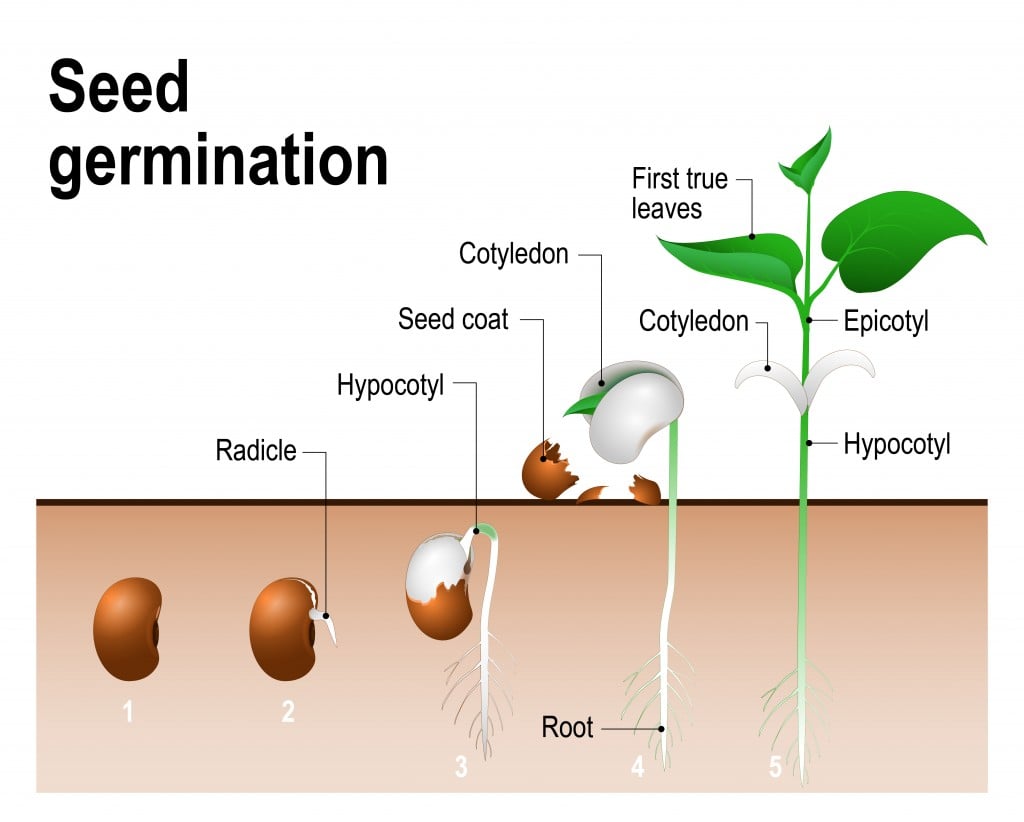
Seed germination occurs when a seed breaks dormancy and begins to sprout and grow. It starts by absorbing water which activates hormones that kickstart the embryo’s growth. The seed coat cracks open allowing the embryonic root to emerge and anchor the seedling. Next, the shoot pokes through the soil towards sunlight to start photosynthesis.
Understanding what’s happening inside the seed during germination helps set realistic expectations for how long the process takes The key requirements for germination are
-
Moisture – The seed needs to absorb enough water to break dormancy but not get waterlogged.
-
Oxygen – Respiration during germination requires oxygen. Good soil aeration facilitates this.
-
Proper temperature – Each seed has an optimal temperature range for sprouting.
-
Sometimes light – Some seeds require light to germinate. Read the packet.
Given the right conditions, the seed embryo will grow into a seedling. But how long does this take?
Factors That Influence Germination Time
Many elements interact to determine the duration of seed germination. This varies not just between plant species, but also individual varieties.
1. Plant Type
-
Annuals: Fast germinators, sprouting within 5-10 days, for quick growth in one season. Radishes, lettuce, and many flowers are annuals.
-
Biennials: Moderate germinators, taking 10-15 days. Carrots and parsley are classic biennials.
-
Perennials: Slower germination, often 2-4 weeks. Perennials prioritize energy storage in seeds. Trees can take months!
2. Seed Viability and Age
-
Fresh, viable seeds germinate better and faster than old seeds.
-
For long viability, store seeds in a cool, dark, and dry place. Refrigeration can extend shelf life.
-
Check expiration dates on seed packets. Older seeds may need more time or not sprout at all.
3. Pre-treatment Methods
Some seeds have built-in dormancy mechanisms that require extra preparation to spark germination:
-
Scarification: Scratching or nicking the seed coat kickstarts germination for seeds with hard outer covers like morning glory.
-
Stratification: Exposing seeds to cold, damp conditions mimics winter. This primes seeds that need a cold spell before sprouting like milkweed.
-
Soaking: Hydrating seeds by soaking overnight helps soften hard seed coats. Bean seeds benefit from soaking before planting.
4. Environmental Factors
Dialing in the right environment is key for optimal germination times:
-
Soil temperature: Each seed has an ideal temperature range. Cooler soils mean longer germination. Peppers need warm soil above 70°F (21°C).
-
Planting depth: Follow instructions on the seed packet. Planting too deeply can hinder germination.
-
Moisture: Water thoroughly after planting, then keep soil moist but not saturated. Too little or too much water delays germination.
-
Oxygen: Well-drained, loose soil provides good oxygen flow. Compacted or overly wet soils impede oxygen access.
-
Sunlight: Some seeds require light to germinate, so plant them on the surface. Others prefer darkness under the soil.
Average Germination Times by Plant
Now that we’ve covered the key factors, here are some general timelines for common plants:
Fast Germinators
- Radish: 3-7 days
- Lettuce: 4-7 days
- Spinach: 7-14 days
- Zinnia: 5-8 days
- Cucumber: 6-10 days
Moderate Germinators
- Tomato: 6-14 days
- Pepper: 10-20 days
- Pumpkin: 7-14 days
- Bean: 7-14 days
- Basil: 5-14 days
Slow Germinators
- Parsley: 14-30 days
- Carrot: 10-20 days
- Pea: 14-21 days
- Pepper: 10-14 days
- Rosemary: 14-21 days
These ranges account for variables in seed freshness, soil temperature, planting depth, and moisture consistency.
Monitoring progress at regular intervals helps ensure seeds have the right conditions for healthy sprouting. If germination lags beyond the typical timeframe, troubleshoot by adjusting temperature, sunlight, or watering as needed.
7 Tips for Faster Seed Germination
Patience is part of gardening, but here are some tricks to help speed up seed germination:
-
Start seeds indoors: The warmer, controlled environment indoors encourages faster sprouting than direct sowing outside.
-
Warm up the soil: Use a heating mat or grow lights to maintain optimal soil temperatures for germination.
-
Prioritize fresh seeds: Check expiration dates and buy seeds each season for higher viability and germination rates.
-
Pre-treat when required: Give seeds like lavender a head start by scarifying or stratifying them as needed.
-
Keep seeds consistently moist: Water soil thoroughly after sowing, then check daily and water as needed to maintain even moisture.
-
Allow proper light exposure: Give light-requiring seeds adequate sunshine or grow lighting. Keep light-shy seeds covered.
-
Aerate soil: Loosen planting areas and ensure good drainage to provide oxygen flow to seeds.
When to Take Action
Germination times are guidelines, not guarantees. If seeds fail to sprout within their typical range, it’s time to intervene:
-
At 2x the average time, gently check seeds for signs of sprouting. If none, replant fresh seeds at the proper depth in pre-warmed soil.
-
At 3x the average time, roots should emerge. If not, replant and create a warmer, humid environment with a heat mat and plastic cover.
-
At 4x the average time, seed viability is low. Switch to a fresh seed packet or new variety. Pre-treat new seeds to encourage germination.
The joy of gardening lies in learning to work with nature’s rhythms. Armed with knowledge and patience, we can overcome germination difficulties. Soon enough, the anticipated seedling will burst forth, rewarding our efforts many times over when the garden comes to fruition.
Special Cases and Techniques:
- Pre-Treatment: Some seeds need special care before they can sprout, like stratification (cold treatment) or scarification (breaking the seed coat). It may take longer for these things to happen, but they are necessary for the seed to sprout.
- Paper Towel Germination Test: If you’re not sure if your seeds will grow or if you want to speed up the process, you can use a damp paper towel and a plastic bag to do a germination test. You can also get a good idea of how long it takes for seeds to sprout in a controlled setting by using this method.
Factors Affecting Germination Time:
- Temperature: Soil temperature plays a crucial role in germination. There are ideal temperature ranges for seeds, and if they are outside of these ranges, they may not germinate at all or only slowly. Peppers, for instance, grow best when it’s warmer (70–85°F or 21–29°C), which is why it can take longer, especially if the soil is cooler.
- Maintaining the right amount of moisture is important for seed germination, but too much can kill the seeds. It’s important to make sure your seeds are damp but not soaked in water. Read my guide on How Often to Water Seedlings to learn more about how to do this.
- Age of the Seed: Older seeds may not germinate as well and may take longer to germinate, if they germinate at all. Always check the expiration date on your seed packets.
- Plant Type: Even within the same species, germination times can be different for each type.
Seed Germination How Long it takes for seeds to GERMINATE
FAQ
How long after planting seeds do they sprout?
Can seeds germinate in 3 days?
Do you water seeds everyday?
How long does it take for seeds to germinate?
It takes about two weeks for most seeds to germinate, while other seeds can take much longer. Seeds should sprout growing within a month of planting when sown in the right conditions. If you don’t see sprouts, then you need to determine the cause. How Long Does It Take For A Seed To Germinate? What Affects Germination Time?
How long does it take for vegetable seeds to sprout?
One easy way to be able to get your garden to this next level is to start your seeds early and consider your plant plan taking into account how long vegetable seeds sprout. The times that it takes vegetable seeds to sprout can depend and change on many different variables, and yet many times it will still end up being a variance of days.
How long does it take a plant to grow from seed?
(Giving them a period of darkness is important, too; it’s when the plants do a lot of their growing!) Many perennials can be easily started from seed and will even blossom the first year! Be patient. It can take anywhere from a few days to a month or more for your seeds to germinate. Again: your seed packets should give you a time estimate!
How long do tomato seeds take to sprout?
At borderline soil temperature, some seeds take weeks or months to sprout. For example, at a soil temperature of 50 degrees Fahrenheit (10 Celsius), tomato seeds take up to 6 weeks to sprout! In this article, we’ll take a look at some common plants and how long their seeds take to sprout. We’ll also talk about how to make it happen a little faster.
- The Ultimate Guide to Growing Strawberries in Raised Beds - August 8, 2025
- No-Dig Garden Beds: The Easiest Way to Grow a Beautiful Garden - August 6, 2025
- How to Protect and Preserve Wood for Raised Garden Beds - August 6, 2025