Cacti are famous for their unique adaptations that allow them to thrive in arid desert environments. Their specialized structures and anatomy set them apart from other plants. In this article, we’ll take a close look at the distinct parts that make up a cactus plant.
The Stem
The stem is the main photosynthetic organ of a cactus plant It is thicker and more succulent than the stems of most plants due to the water-storing tissue inside This enables cacti to survive long periods of drought.
Cactus stems come in different shapes:
-
Round and cylinder-shaped stems are seen in barrel cacti,
-
Flattened oval pads are found in prickly pears and cholla.
-
Columnar cacti like saguaro have tall, vertical stems.
The outer surface of the stem may be smooth or have protrusions like ribs, tubercles, and ridges. A waxy coating helps reduce water loss.
Areoles
Unique to cacti, areoles are small cushion-like structures scattered across the stem surface. They produce spines, flowers, branches, and leaves (when present). New growth originates from areoles.
Spines
Spines are highly modified leaves that emerge from the areoles. Their main functions are:
-
Deterring herbivores
-
Providing shade to reduce water loss
-
Gathering moisture through condensation
Spines come in many shapes like needles, barbs, hooks, and clubs. They may be fixed or detachable. Some cacti also have fine, hair-like spines called glochids.
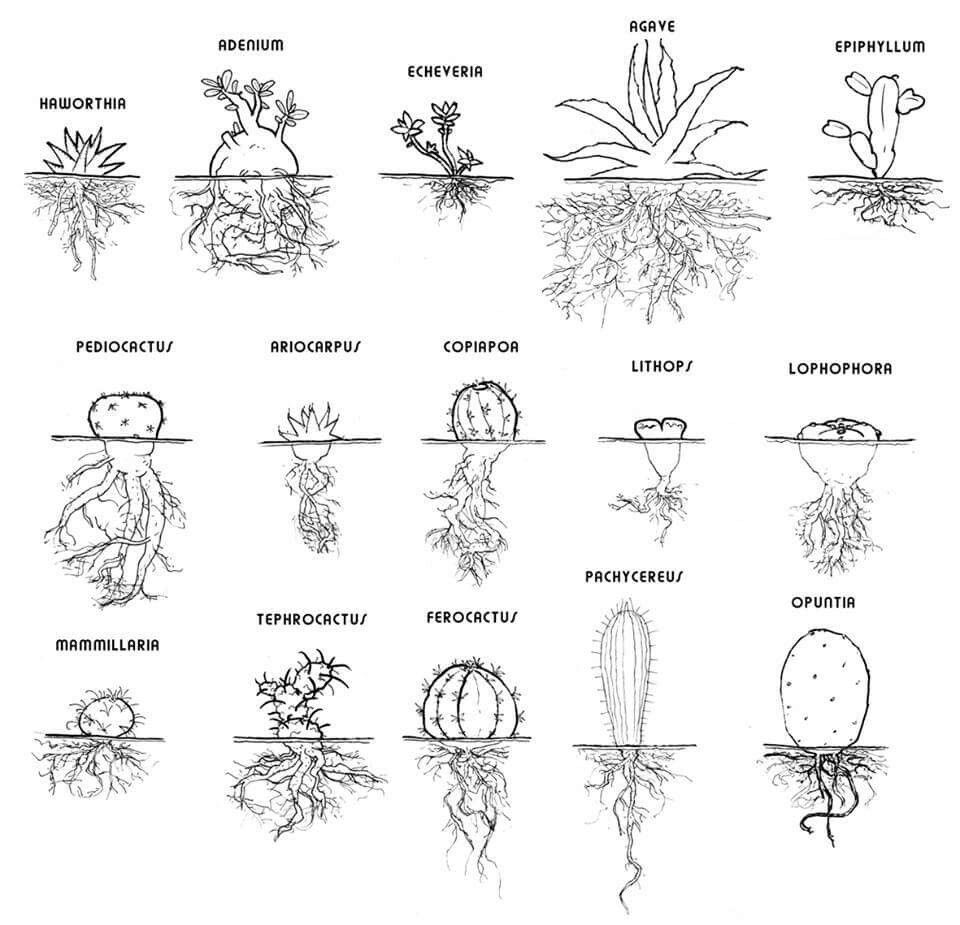
Roots
Cactus roots are generally shallow and widespread to absorb as much moisture as possible when it rains. Fibrous root hairs efficiently take up water near the soil surface. Taproots give some species added stability.
Leaves and Flowers
Most cacti don’t have true leaves. In those that do, the leaves are small and succulent, like the rounded leaves of Pereskia. Flowers are large and brightly colored, ranging from white to yellow, pink, orange, red, and purple. They bloom singly at the end of stems and live for only a day or two.
Fruit
After pollination, the cactus flower detaches from the ovary while the ovary develops into a fleshy, berry-like fruit. The fruit contains many small seeds and juice. Some cactus fruits are edible, like the prickly pear.
Specialized Features
Some cacti have unique adaptations to their harsh environments. For example:
-
Epiphytic cacti have flattened stems for absorbing moisture and clinging to tree branches.
-
Taproots give giant columnar cacti like saguaro stability in the desert floor.
-
Ribbed stems expand and shrink to store or conserve water.
-
Trichomes reflect sunlight and reduce air flow over the surface.
-
Camouflage – Some cacti blend into their rocky surroundings.
Growth Habit
The growth habit of a cactus depends on the species. Some common habits include:
-
Tree-like columns up to 40 feet tall
-
Shrubs made up of cylindrical stems
-
Low mats that spread across the ground
-
Vine-like epiphytes with trailing or hanging stems
-
Forming clusters of round, globe-shaped stems
Reproduction
Cacti mainly reproduce by seed. They can also propagate vegetatively by:
-
Rhizomes – underground horizontal stems
-
Offsets – clonal “pups” emerging at the base
-
Cuttings – segments or pads that root after separation
-
Grafting – joining the top of one cactus species to the bottom of another
This gives an overview of the unique structures and forms of cactus plants. Specialized stems, lack of leaves, spines for protection, and adaptations for water storage allow these incredible plants to thrive in hot, dry environments. The distinctive parts of a cactus all contribute to its survival where other plants cannot.
Parts of a plant (cactus)
FAQ
What are the sharp parts of a cactus called?
What does a cactus stem look like?
What is the anatomy of a cactus plant?
What is the name of the root of a cactus?
- The Ultimate Guide to Growing Strawberries in Raised Beds - August 8, 2025
- No-Dig Garden Beds: The Easiest Way to Grow a Beautiful Garden - August 6, 2025
- How to Protect and Preserve Wood for Raised Garden Beds - August 6, 2025